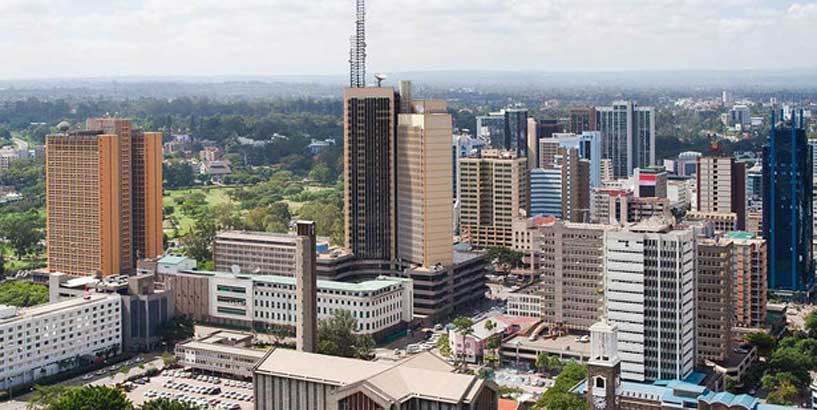
Kenya is a vital business hub and a strategic point of entry into the Eastern Africa market. This fact, coupled with the growing population and the expanding infrastructure, presents excellent opportunities for foreign investors in the Kenyan real estate industry. There is also a large number of informal settlements in Kenya with nearly 61% of the people who live in Nairobi, the capital city of Kenya, living in informal settlements.
Demand for housing in Kenya is on the rise. A notable undersupply of formal housing in Kenya has been caused by the increased rise of middle-class individuals between ages 24 and 35. The vision 2030 of Kenya estimates that more than 80% of the Kenyan population will migrate from rural areas to urban areas by 2030, an indication that demand for real estate will continue to increase in urban centers in the coming years. This is an important reason why foreign investors should consider investing in this industry.
Most local investors face a myriad of financial hurdles that limit prospective buyers from owning property. The mortgage market in Kenya has not matured yet; for this reason, foreign investors with strong financial resources can more easily venture into the real estate market than most local investors are able to. Financing is a major concern to the Kenya property developers Association (KPDA). KPDA admits that most of its members find it tricky to venture into the real estate market due to a lack of funding. Although the association has continued to urge financial companies to open their coffers to prospective homeowners, this plea is far from being implemented. Under the prevailing circumstances, therefore, foreign investors have an upper hand in the real estate market in Kenya.
Demand for housing in Kenya can also be attributed to population growth, demand for executive offices, and warehousing. Foreign investment in other sectors of the economy such as the hospitality industry, construction, supply chain, and manufacturing, among others, have contributed immensely to the growth of opportunities in the Kenyan real estate market. The increase in high net worth investors who are venturing into other forms of investments such as shopping malls, hotels, and offices makes real estate a profitable venture in Kenya.
Some international investors have identified this need and are moving swiftly to meet it. Top Chinese companies such as China Wu Yi Co. Ltd., AVIC international, and Twyford Ceramics have invested in projects estimated at more than Ksh 50 billion to expand their businesses, revolutionizing the Kenyan real estate industry. An Indian firm, Shapoorji Pallonji, in a joint venture with another firm called Actis has committed Ksh 12 billion in real estate investment in the country. Xterra Capital Advisors, based in Mauritania, has also taken a stake in the Kenyan real estate market. The firm has invested approximately KSh20 billion in real estate in retail, office, hospitality, and industrial properties.
Investors should understand the rules and regulations that govern land ownership in the country before investing in the Kenyan real estate market. In Kenya, there are three categories of land. Pubic land is reserved for public use or for protecting the environment. This land is managed by the National Land Commission. A developer can acquire public land after applying to the National Land Commission. Public land must be utilized for the purposes intended in the declaration, or it will be taken back by the government.
Private land is the land held by Kenyan Natives, or legal persons; this land is managed by the Ministry of Lands, tasked with the registration of any interest in private land. The Land Registration Act provides that transfer, acquisition, freehold, or leasehold of private land should be registered with the local land registry. The Kenyan constitution stipulates that foreign ownership of private land is restricted to a leasehold for a maximum of 99 years. The third category of land in Kenya is the community land, which is held by communities based on ethnicity, culture, or similar community interests. More details on the rules and regulations governing land ownership in Kenya will be covered in subsequent articles.
Real estate in the current Kenyan market favors foreign investors who know how to analyze the cyclical nature of real estate investments. Local developers are presently experiencing a cash crunch, mostly because of Covid-19. This means that any foreign investor with significant financial resources can plan, develop, and complete a project in Kenya with ease.
Investing in the real estate market in Kenya is not risk-free. Foreign investors should take into account some macro risks that accompany real estate investments in the country. Such risks include government debt that might impact the inflation rates in the country and untrustworthy real estate agents. As such, investors should research trustworthy agents to handle their transactions. There are many credible, affordable real estate agents in Kenya such as Knight Frank Kenya, Homes Universal, Ramugo Project Management, and Hass Consult Limited. Keep checking this space for more insight into the most reliable real estate agents in the country and other real estate investment information in Kenya.